Firstly, in order to identify Legionnaires disease as a significant hazard it is important to know and understand the factors that affect the rate of growth and transmission of legionella as well as any potential exposure to the hazard.
The four main factors that influence the growth of legionella are;
1. TEMPERATURE
2. WATER FLOW / STAGNATION
3. PARTICULATE MATTER
4. NUTRIENT SUPPLY
TEMPERATURE
1. Legionella exists in low numbers when the temperature is below 20°C
2. Between 20°C and 37°C the growth is rapid and slows down as it reaches 45°C
3. At 50°C 90% of legionella dies off within two hours and at 60°C legionella are killed off within two minutes.
WATER FLOW STAGNATION
Low or no flow rate of a fluid may cause stagnation which will encourage the growth of legionella.
PARTICULATE MATTER
Particulate matter may offer protection to the legionella bacteria where they may be killed off in adverse conditions.
NUTRIENT SUPPLY
Common organisms such as bacteria serve as a nutrient for legionella.
USING A PLATE HEAT EXCHANGER TO REDUCE THE RISK OF LEGIONNAIRES DISEASE
Because a Plate Heat Exchanger instantaneously heats up fluids and does not have any storage they practically eliminate the possibility of any dangerous bacteria growth such as legionella.
A typical Plate Heat Exchanger can heat up domestic hot water from 10°C to 60°C instantaneously at a continuous flow rate of 5 L/S.
The AEL Plate Heat Exchanger plates are made from stainless steel with a corrugated profile which creates turbulence as the fluid flows through the unit which also scrubs and also helps to reduce any particulate deposits forming on the plates.
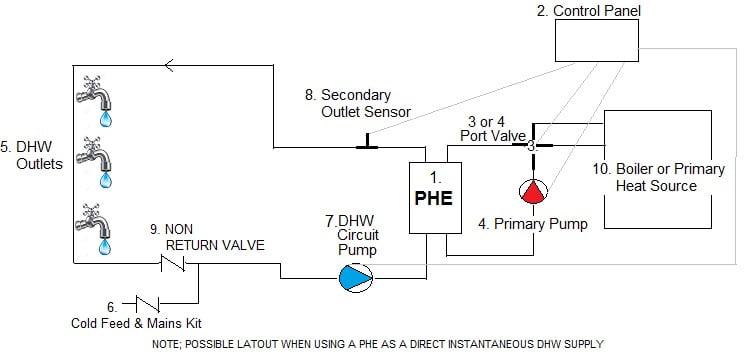
It is worth noting that using a plate heat exchanger can practically eliminate legionella from the most common sources which have been found to be:
- COOLING TOWERS and EVAPOURATOR CONDENSERS.
- HOT WATER SYSTEMS
- HUMIDIFIERS and AIR WASHERS
A GUIDE ON HOW TO MANAGE THE RISK OF LEGIONELLA
It is important that every installation has a well thought through scheme to prevent or minimise the risks of legionella.
It is important that a responsible person is employed to manage and implement precautions.
It is important that records are kept of the precautions taken.


